latest articles
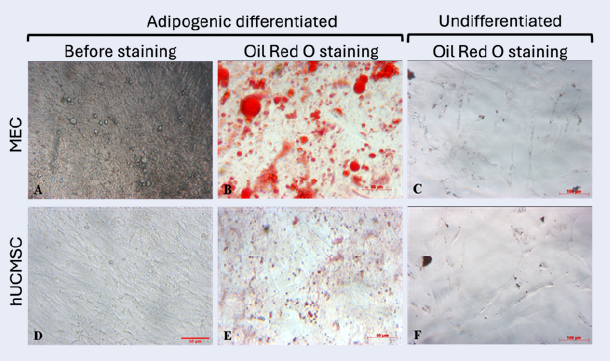
Efficient Enrichment of Muse Cells from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Collagenase and Hypoxic Stress
by Minh Le
T.,
Bao Phan
N.,
Tuan Truong
K.,
Bich Vu
N.
Summary: Muse (multilineage-differentiating stress-enduring) cells are a pluripotent subpopulation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), characterized by their stress tolerance and significant potential in regenerative medicine. However, their low abundance poses challenges for isolation. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of severe stress conditions—including low temperature, severe hypoxia, and collagenase treatment (LHC)—in isolating Muse cells.
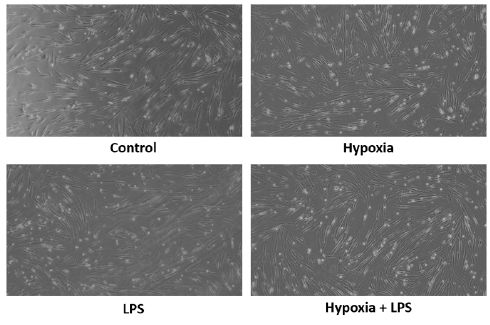
Potential Protection of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Against Oxidative Stress With Hypoxia Preconditioning and Lipopolysaccharide Exposure
by Fajri
F., M., E.,
Yuhendri
V., M.,
Elmi
E.,
Saputra
N., P., K.,
Arfianti
A.
Summary: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are among the most promising therapeutic options for degenerative diseases. However, the low viability and prolonged doubling time of MSCs during ex vivo expansion remain obstacles in their application in MSC-based therapies. MSC preconditioning has been considered a potential strategy to overcome challenges in MSC culture and to increase the therapeutic effects of MSCs. To mimic an inflammatory microenvironment and enhance stress resilience, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was combined with hypoxia preconditioning. The aim of this study was to examine the effects of hypoxia and LPS preconditioning on viability, population doubling time, and expression levels of antioxidant genes in MSCs.
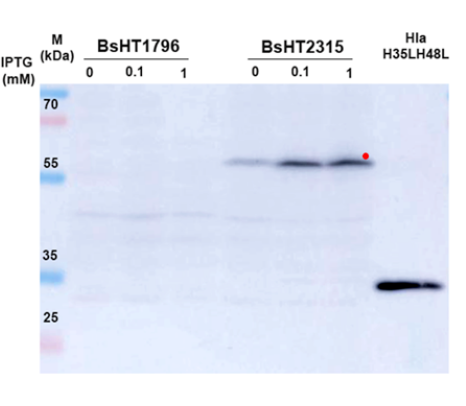
Surface Display of Alpha-Toxin HlaH35LH48L on Bacillus subtilis Cells for Oral Vaccine Delivery in Mice
by Nguyen
N.,
Duong
L.,
Nguyen
A.,
Dinh
T.,
Phan
T.,
Nguyen
H.
Summary: Surface display of proteins on Bacillus subtilis has emerged as a promising strategy in vaccinology, leveraging its safety, gastrointestinal resilience, and capacity for efficient antigen presentation. Targeting Staphylococcus aureus, a pathogen reliant on alpha-toxin (Hla) for virulence, this study focuses on a detoxified variant, HlaH35LH48L, to potentially neutralize toxicity while preserving immunogenicity. We investigated B. subtilis as an oral vaccine vector to display HlaH35LH48L and elicit mucosal and systemic immune responses in mice.
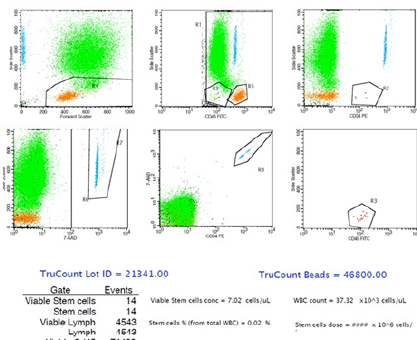
Plerixafor for Stem Cell Mobilization in Autologous Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Case Series of Lymphoma Patients from a Northeastern Malaysian Teaching Hospital
by Zulkeflee
R.,
Hassan
M., N.,
Saidin
N., I., S.,
Akbar
N., A., N.,
Abdullah
M.,
Husin
A.,
Abdullah
A., D.,
Sidik
M. A.
Summary: In recent years, plerixafor, a CXCR4 chemokine receptor inhibitor, has emerged as a promising agent for the mobilization of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) when combined with other mobilizers such as granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) and chemotherapy in patients with multiple myeloma and lymphoma undergoing autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (APBSCT). Our facility has recently implemented plerixafor as a specialized rescue treatment in lymphoma patients who are at risk or have experienced mobilization failure with G-CSF.
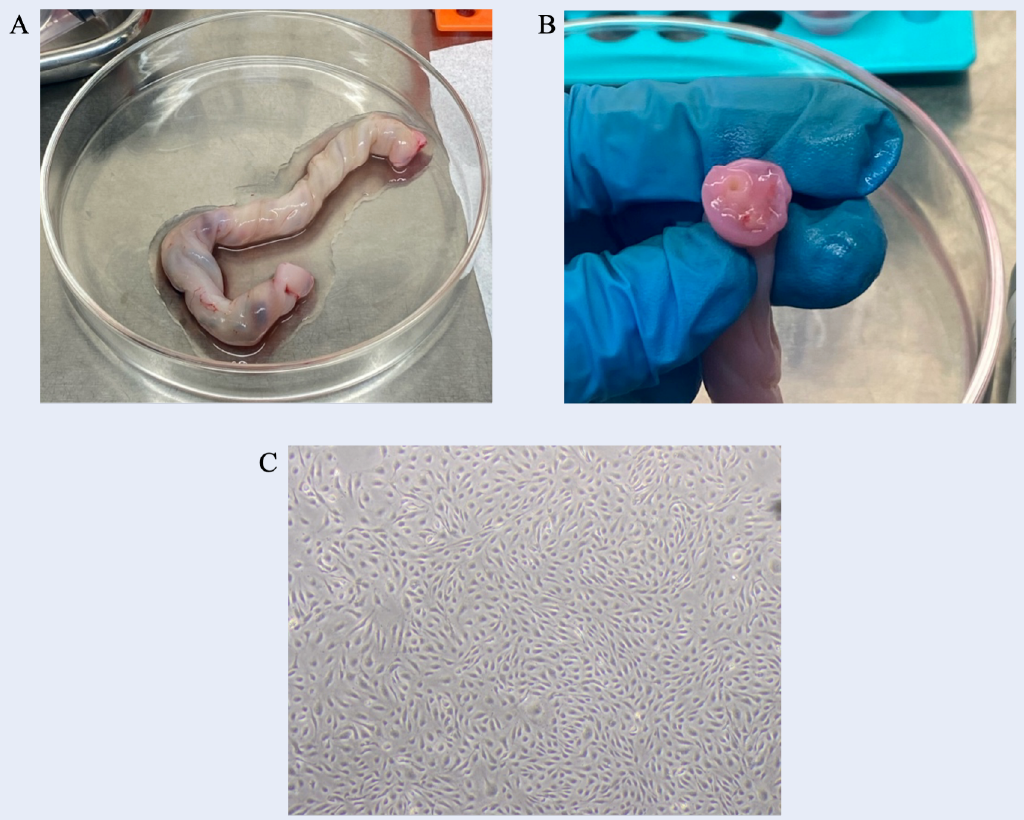
Human In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models in Angiogenesis Research: Advances and Challenges
by Razmi
M.,
Ugusman
A.,
Sulaiman
N.,
Ahmad
M.,
Abdul-Ghani
S.,
Ismail
M.,
Mohamad Anuar
N. N.
Summary: Angiogenesis, the process of new blood vessel formation, is a complex phenomenon that plays a crucial role in various physiological and pathological processes, including embryonic development, tissue repair, vascular homeostasis, and tumor microenvironments. The utilization of human in vitro and ex vivo models to study angiogenesis is an actively investigated area that holds great promise for offering novel insights and prospects for developing methods to treat angiogenesis-related diseases, such as cancer and cardiovascular disorders. Combining in vitro and ex vivo models using human samples can enhance the understanding of the complex process of angiogenesis in the human body. This integrative strategy facilitates a holistic exploration of angiogenesis, bridging the gap between simplified in vitro systems and the complexities inherent in in vivo settings, thereby augmenting the translational prospects of research outcomes for clinical applications. However, ethical constraints, inherent individual variability in human samples, challenges in obtaining tissue samples, technical issues in tissue handling, and the high cost involved are key limitations to consider.
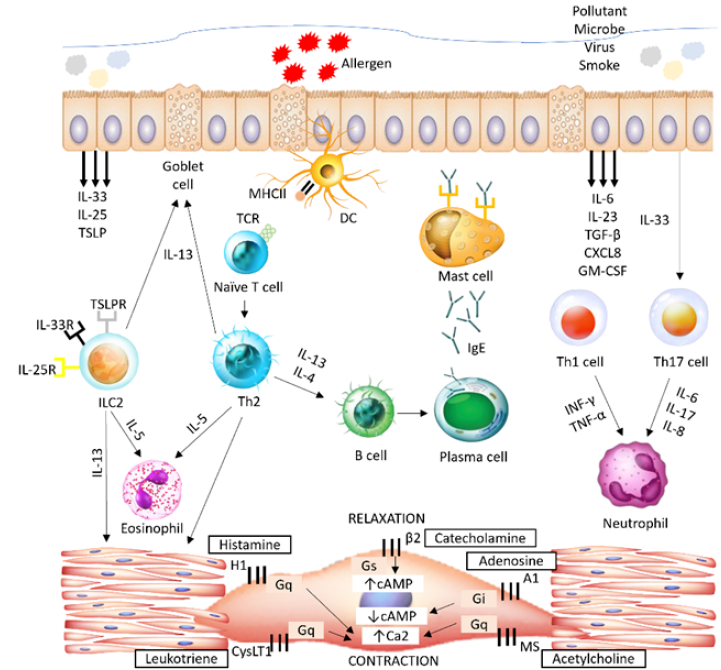
Murine Models of Allergic Asthma: Methodological Insights into Allergen Sensitization and Challenge Protocols
by Bushra
S., M., R.,
Nurul
A. A.
Summary: Asthma represents a chronic inflammatory airway disease with a steadily increasing global prevalence in recent decades. Animal models have proven invaluable in elucidating the underlying disease mechanisms and identifying innovative therapeutic approaches. The murine model is extensively used to investigate key characteristics of allergic asthma, including airway inflammation, airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), and airway remodeling. Classic protocols involving sensitizing and challenging animals with different types of allergens and modes of administration are major factors in inducing asthmatic features in a mouse model. The present review critically analyzes the commonly used sensitization and allergen challenge protocols for inducing acute and chronic inflammation in the airways of mouse models of asthma, emphasizing their potential in advancing therapeutic development for allergic asthma studies.
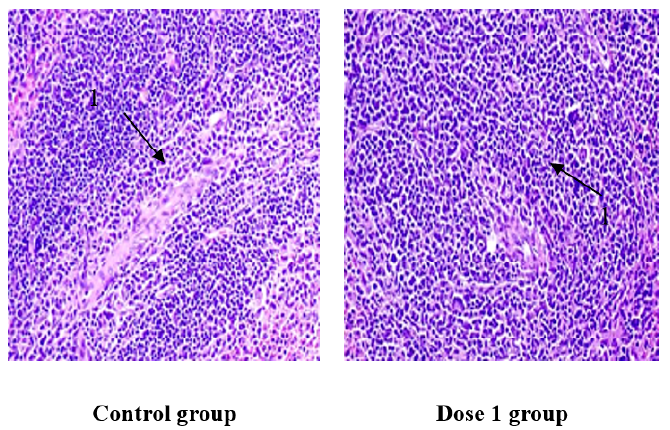
Investigating the Immunomodulatory Effects of Tieu U Hoan Herbal Preparation in a Murine Hepatocellular Carcinoma Model
by Luu
H., T., T.,
Nguyen
H. S.
Summary: Traditional medicine treatments (TMT) are widely recognized as effective complementary therapies in cancer care, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Tieu u hoan (TUH), an herbal formulation derived from TMT principles and clinical expertise, has shown promise in preclinical and clinical studies as a supportive therapy for HCC. This study investigates the immunomodulatory effects of TUH in immunodeficient nude mice engrafted with human Hep3B liver cancer cells.
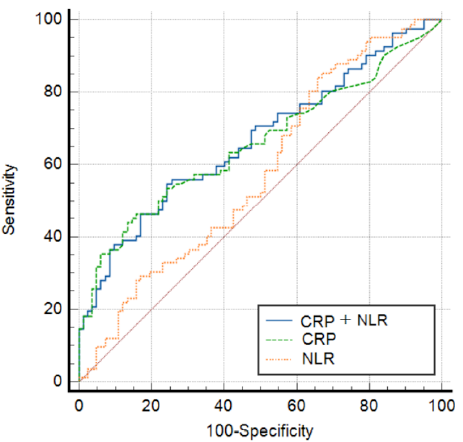
Assessing inflammatory markers, C-reactive protein and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, in atrial fibrillation and normal sinus rhythm: A comparative analysis
by Chang
J.,
Jung
B.,
Kim
J.
Summary: C-reactive protein (CRP) has shown associations with multiple cardiovascular disorders, including atrial fibrillation (AF). Similarly, the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is gaining recognition as a potential prognostic factor in cardiovascular health. Although AF has been widely studied, much of the current research emphasizes individuals of White ethnicity, underscoring the need for further investigation across more ethnically diverse populations.
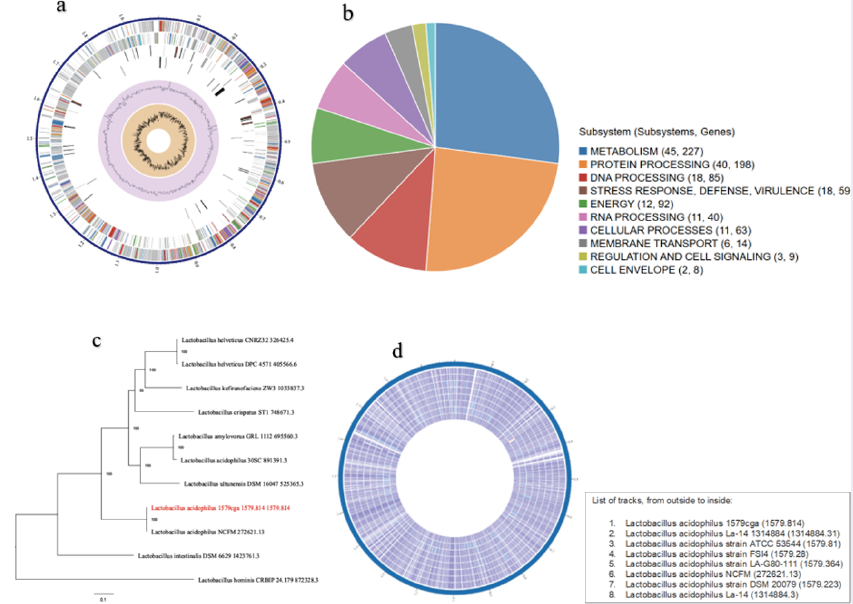
Peptides from hypothetical proteins of Lactobacillus acidophilus induce IL-4 and IL-10
by Adejumo
I.,
Adebiyi
O.
Summary: Commensal bacteria used for probiotics usually pose no health risk. However, the functional mechanisms of these probiotics are not fully understood, thereby necessitating new studies such as this. The study aimed to understand the functional mechanisms of microbial probiotics and characterize their uncharacterized hypothetical proteins. In this study, the probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus genome was explored for antibiotic resistance genes, characterization of hypothetical proteins, and their relationships with cytokine interleukin-4 (IL-4) and cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10). The genome has an average G+C content of 34.71 and 1,991,579 bp. It has 1,909, 61, and 12 protein-coding sequences, transfer RNA, and ribosomal RNA genes, respectively. Peptides from QHP2 and QHP5 induce IL-4 and IL-10. They are antigenic, nontoxic, and nonallergenic. This study provides insights into better understanding the functional mechanisms of microbial probiotics and lays a solid background for future studies that may focus on sustainable therapeutic feed additives, food supplements, and vaccine development from the hypothetical proteins of Lactobacillus acidophilus.
Hydrogel dressings: Revolutionizing burn care with innovative wound healing technology
by Huynh
P.
Summary: Severe burns result in deep and extensive wounds that are associated with a high mortality rate. While wound closure is an essential part of the treatment for such injuries, merely providing superficial coverage of the defect is inadequate. Adequate reconstruction requires repairing the damaged area from the innermost layers outward. Hydrogel dressings have become a very popular choice due to their unique properties: contributing to wound moisture, cooling and soothing, and autolytic debridement. This type of dressing offers the potential to overcome disadvantages of traditional treatments and allows partial skin regeneration. This review aims to outline the benefits of hydrogel dressings, emphasizing their role in wound healing and tissue regeneration, particularly in the context of chronic burn wounds. The discussion also covers how these dressings may address current shortcomings in wound care and provides a focused overview of specific attributes and potential future improvements in the field. This review enhances the general understanding of their therapeutic implications by examining the benefits of hydrogel dressings.
Antitumor effect of lavender essential oil-synthesized nanoparticles against MCF7 and SKBR3 cancer cell lines: Cytotoxicity and gene expression analysis
by Mojodi
E.,
Sabbagh
S.,
Shahamiri
K.,
Rajabi
M.
Summary: Lavandula angustifolia L. (Lamiaceae family) displays notable cytotoxic properties against bacteria and fungi, as well as antioxidant activity. Recently, drug delivery systems for cancer therapy have focused on novel carrier designs that demonstrate high efficiency and reduced side effects. The encapsulation and delivery of bioactive agents through essential oils has emerged as a new strategy in cancer research. This study aimed to investigate the effects of nanoparticles synthesized using L. angustifolia essential oil on MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 breast cancer cell lines.

Effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma and peripheral blood-derived very small embryonic-like stem cells in Parkinson’s disease management
by Anwar
S.,
Hassan
A.,
Waseem
H.,
Baeesa
S.,
Alkhotani
A.,
Bamaga
A.,
Najjar
A.,
Karami
M.,
Badahdah
A.,
Basheikh
M.,
Alkhotani
A.,
Shaukat
G.,-a-R.,
Tirmzi
F.,
Kurdi
M.
Summary: Stem cell-based therapies for Parkinson's disease (PD) represent a promising frontier in regenerative medicine. This study assesses the efficacy of regenerative treatments, specifically platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and peripheral blood-derived very small embryonic-like (PBD-VSEL) stem cell therapy, in managing PD.
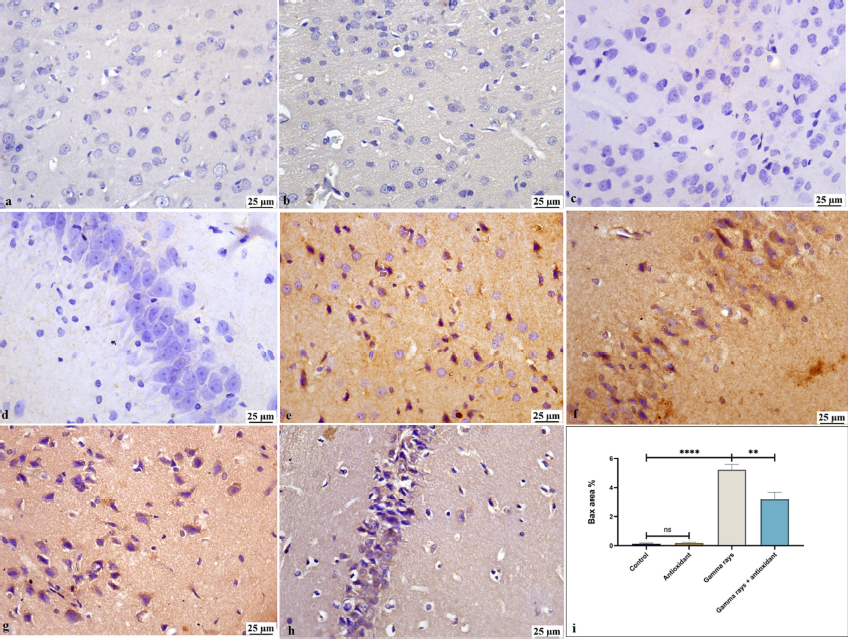
Evaluation of the effect of arabinogalactans extracted from matcha on gamma radiation-induced brain damage in rats
by Awad
M.,
El Adham
E.,
Hassan
A.
Summary: Radiation has adverse effects on brain tissue. Natural products have anti-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory properties. This study investigates the protective effect of alginate extract from matcha against gamma radiation damage.
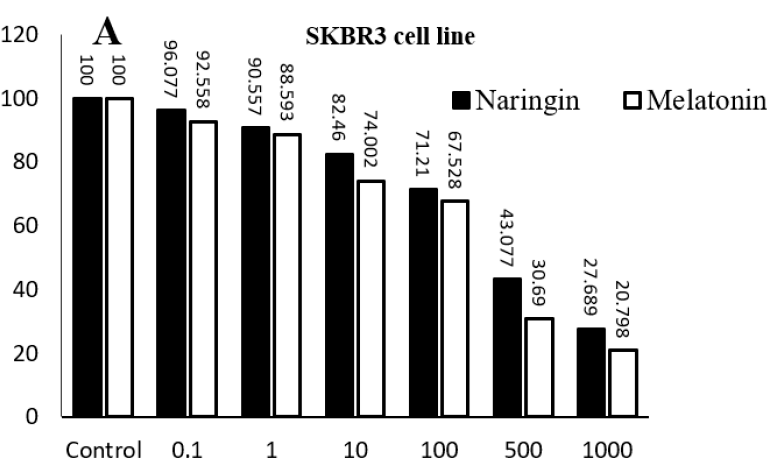
Exploring the therapeutic potential of naringin and melatonin in breast cancer: A focus on SKBR3 and MCF-7 cell lines
by Azizpour
M.,
Changizzadeh
B.,
Golbashirzadeh
M.,
Moradzadegan
A.
Summary: Breast cancer is a significant global health issue, particularly in women, and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related deaths in Iran. This study investigates the anticancer effects of naringin and melatonin on SKBR3 (HER2+) and MCF-7 (HER2-) breast cancer cell lines.
Journal Collections

Covid-19 publications
Journal Supplements
Conference Abstracts
Journal Collections

Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine
Special Issues

Special Issues
Journal Collections

Natural Extract
Publication Awards

The best original research articles
Editors' quote

Phuc Van Pham, Editor-in-Chief
Affiliation

Why publish with Biomedical Research and Therapy



 Biomedpress
Biomedpress




