latest articles
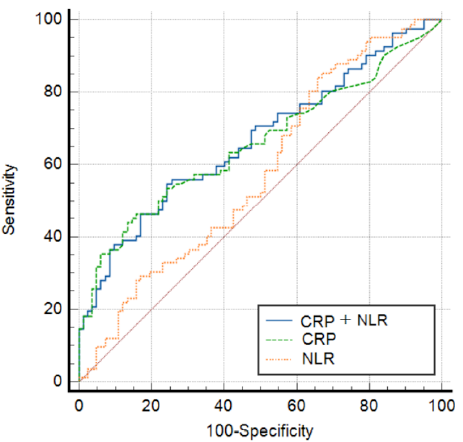
Assessing inflammatory markers, C-reactive protein and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, in atrial fibrillation and normal sinus rhythm: A comparative analysis
by Chang
J.,
Jung
B.,
Kim
J.
Summary: C-reactive protein (CRP) has shown associations with multiple cardiovascular disorders, including atrial fibrillation (AF). Similarly, the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is gaining recognition as a potential prognostic factor in cardiovascular health. Although AF has been widely studied, much of the current research emphasizes individuals of White ethnicity, underscoring the need for further investigation across more ethnically diverse populations.
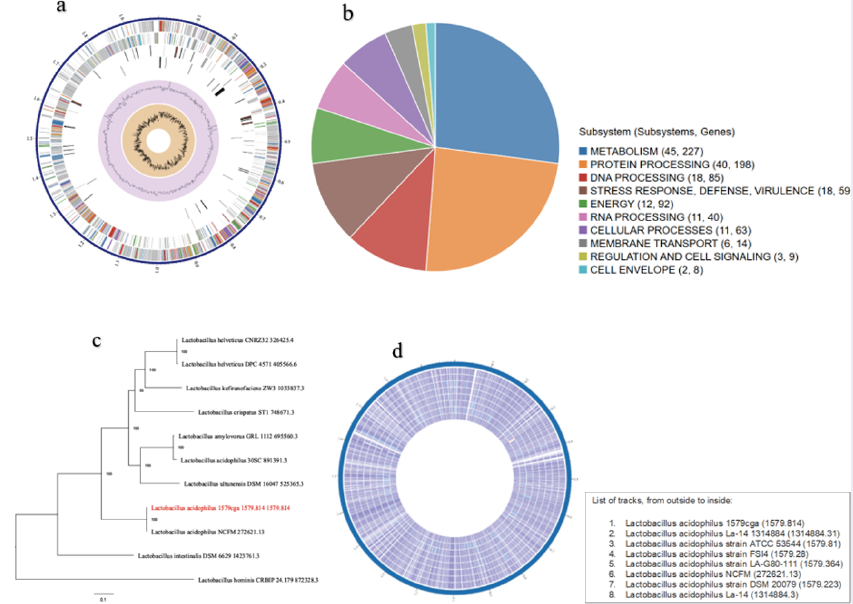
Peptides from hypothetical proteins of Lactobacillus acidophilus induce IL-4 and IL-10
by Adejumo
I.,
Adebiyi
O.
Summary: Commensal bacteria used for probiotics usually pose no health risk. However, the functional mechanisms of these probiotics are not fully understood, thereby necessitating new studies such as this. The study aimed to understand the functional mechanisms of microbial probiotics and characterize their uncharacterized hypothetical proteins. In this study, the probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus genome was explored for antibiotic resistance genes, characterization of hypothetical proteins, and their relationships with cytokine interleukin-4 (IL-4) and cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10). The genome has an average G+C content of 34.71 and 1,991,579 bp. It has 1,909, 61, and 12 protein-coding sequences, transfer RNA, and ribosomal RNA genes, respectively. Peptides from QHP2 and QHP5 induce IL-4 and IL-10. They are antigenic, nontoxic, and nonallergenic. This study provides insights into better understanding the functional mechanisms of microbial probiotics and lays a solid background for future studies that may focus on sustainable therapeutic feed additives, food supplements, and vaccine development from the hypothetical proteins of Lactobacillus acidophilus.
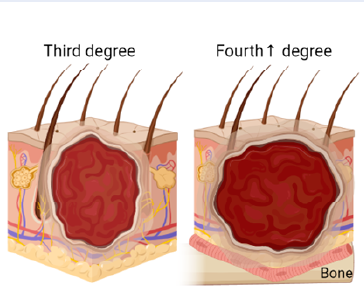
Hydrogel dressings: Revolutionizing burn care with innovative wound healing technology
by Huynh
P.
Summary: Severe burns result in deep and extensive wounds that are associated with a high mortality rate. While wound closure is an essential part of the treatment for such injuries, merely providing superficial coverage of the defect is inadequate. Adequate reconstruction requires repairing the damaged area from the innermost layers outward. Hydrogel dressings have become a very popular choice due to their unique properties: contributing to wound moisture, cooling and soothing, and autolytic debridement. This type of dressing offers the potential to overcome disadvantages of traditional treatments and allows partial skin regeneration. This review aims to outline the benefits of hydrogel dressings, emphasizing their role in wound healing and tissue regeneration, particularly in the context of chronic burn wounds. The discussion also covers how these dressings may address current shortcomings in wound care and provides a focused overview of specific attributes and potential future improvements in the field. This review enhances the general understanding of their therapeutic implications by examining the benefits of hydrogel dressings.
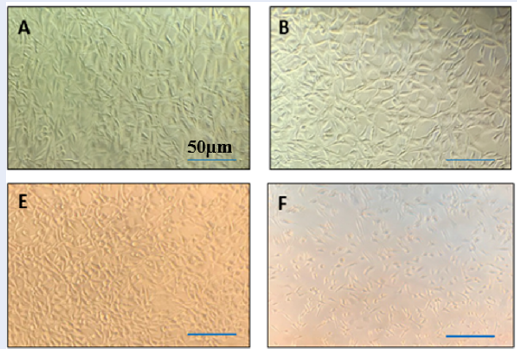
Antitumor effect of lavender essential oil-synthesized nanoparticles against MCF7 and SKBR3 cancer cell lines: Cytotoxicity and gene expression analysis
by Mojodi
E.,
Sabbagh
S.,
Shahamiri
K.,
Rajabi
M.
Summary: Lavandula angustifolia L. (Lamiaceae family) displays notable cytotoxic properties against bacteria and fungi, as well as antioxidant activity. Recently, drug delivery systems for cancer therapy have focused on novel carrier designs that demonstrate high efficiency and reduced side effects. The encapsulation and delivery of bioactive agents through essential oils has emerged as a new strategy in cancer research. This study aimed to investigate the effects of nanoparticles synthesized using L. angustifolia essential oil on MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 breast cancer cell lines.

Effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma and peripheral blood-derived very small embryonic-like stem cells in Parkinson’s disease management
by Anwar
S.,
Hassan
A.,
Waseem
H.,
Baeesa
S.,
Alkhotani
A.,
Bamaga
A.,
Najjar
A.,
Karami
M.,
Badahdah
A.,
Basheikh
M.,
Alkhotani
A.,
Shaukat
G.,-a-R.,
Tirmzi
F.,
Kurdi
M.
Summary: Stem cell-based therapies for Parkinson's disease (PD) represent a promising frontier in regenerative medicine. This study assesses the efficacy of regenerative treatments, specifically platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and peripheral blood-derived very small embryonic-like (PBD-VSEL) stem cell therapy, in managing PD.
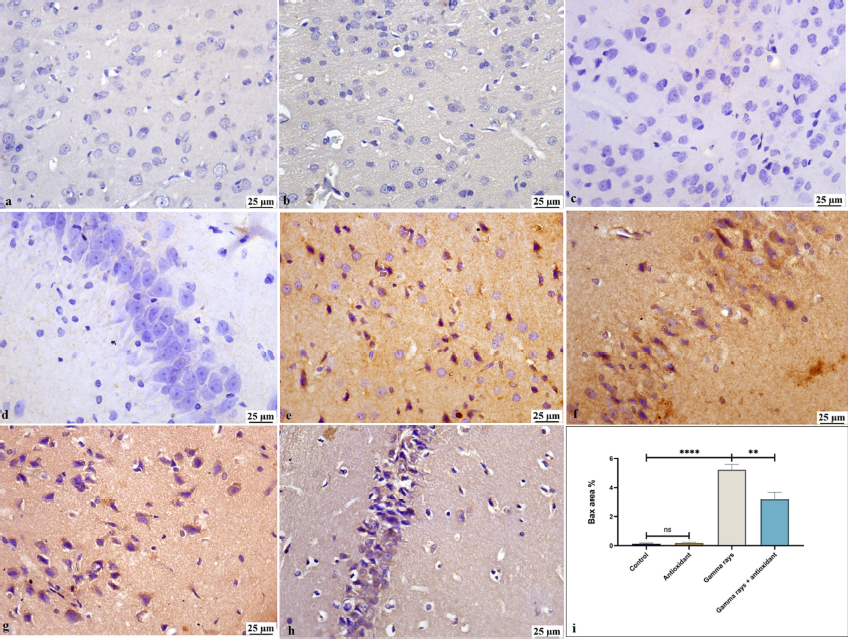
Evaluation of the effect of arabinogalactans extracted from matcha on gamma radiation-induced brain damage in rats
by Awad
M.,
El Adham
E.,
Hassan
A.
Summary: Radiation has adverse effects on brain tissue. Natural products have anti-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory properties. This study investigates the protective effect of alginate extract from matcha against gamma radiation damage.
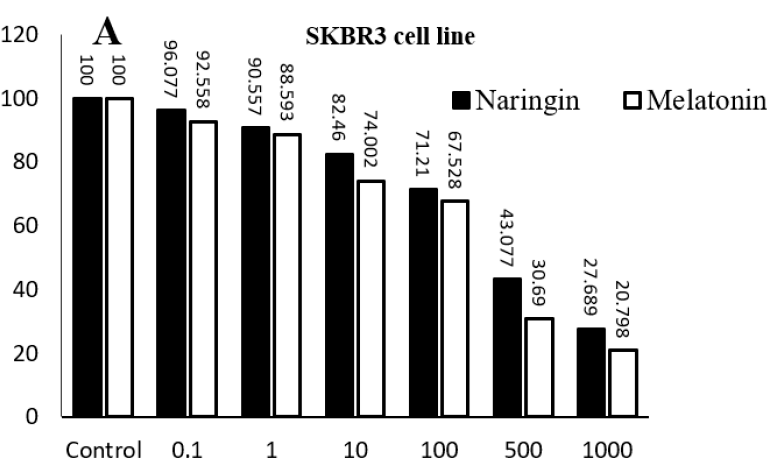
Exploring the therapeutic potential of naringin and melatonin in breast cancer: A focus on SKBR3 and MCF-7 cell lines
by Azizpour
M.,
Changizzadeh
B.,
Golbashirzadeh
M.,
Moradzadegan
A.
Summary: Breast cancer is a significant global health issue, particularly in women, and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related deaths in Iran. This study investigates the anticancer effects of naringin and melatonin on SKBR3 (HER2+) and MCF-7 (HER2-) breast cancer cell lines.
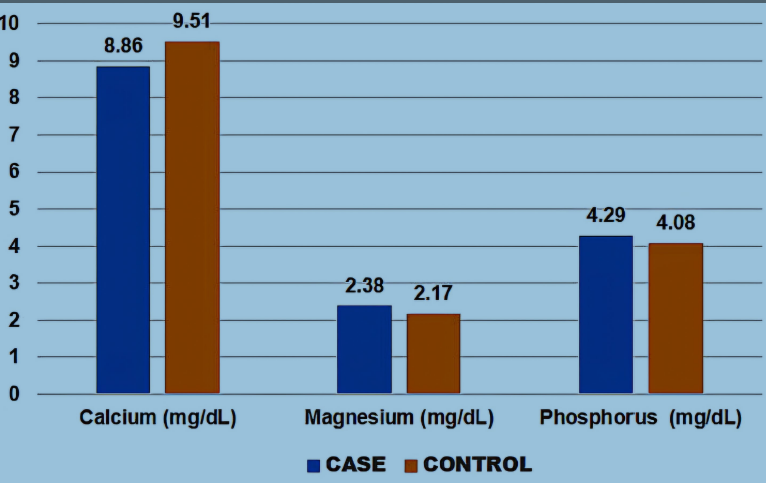
Assessment of thyroid profile and mineral status in patients with hypothyroidism – A hospital based case-control study
by Ramesh
N.,
Kumar
D.,
Selvarajan
S.,
Krishnamurthy
S.,
Sathyamurthy
S.
Summary: Thyroid hormones are major contributors to numerous physiological processes in the body. Thyroid disorders are frequently associated with an imbalance in the homeostasis of calcium and phosphorus. The objective of this study is to evaluate and compare the mineral status of hypothyroid patients and euthyroid controls by determining the serum levels of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. The aim is to identify any significant differences in the concentrations of these minerals between hypothyroid individuals and healthy controls, thereby contributing to a better understanding of the potential metabolic disturbances associated with hypothyroidism.
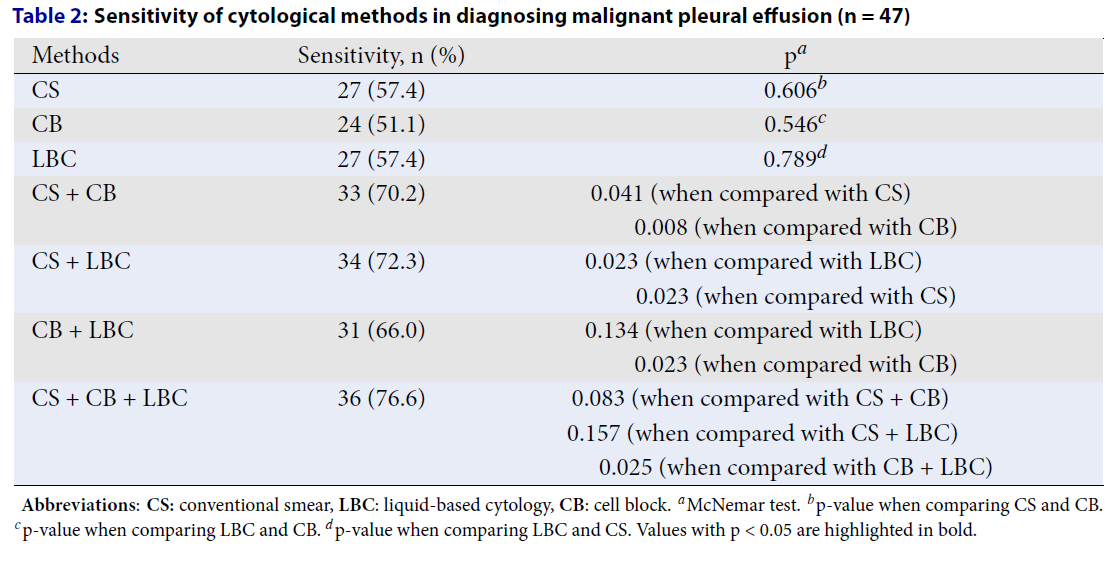
The diagnostic value of liquid-based cytology of pleural fluid in malignant pleural effusion: A prospective study
by Vu-Hoai
N.,
Le-Phu
N.,-T.,
Nguyen-Dang
K.,
Duong-Minh
N.,
Tran-Ngoc
N.,
Dang-Vu
T.,
Lam-Quoc
D.
Summary: Pleural effusion (PE) is commonly observed in clinical practice. Conventional smear (CS), cell block (CB), and liquid-based cytology (LBC) of pleural fluid are used to guide the diagnosis of malignant pleural effusion (MPE). However, the effectiveness of these cytological techniques, whether used alone or in combination, is still not well established.
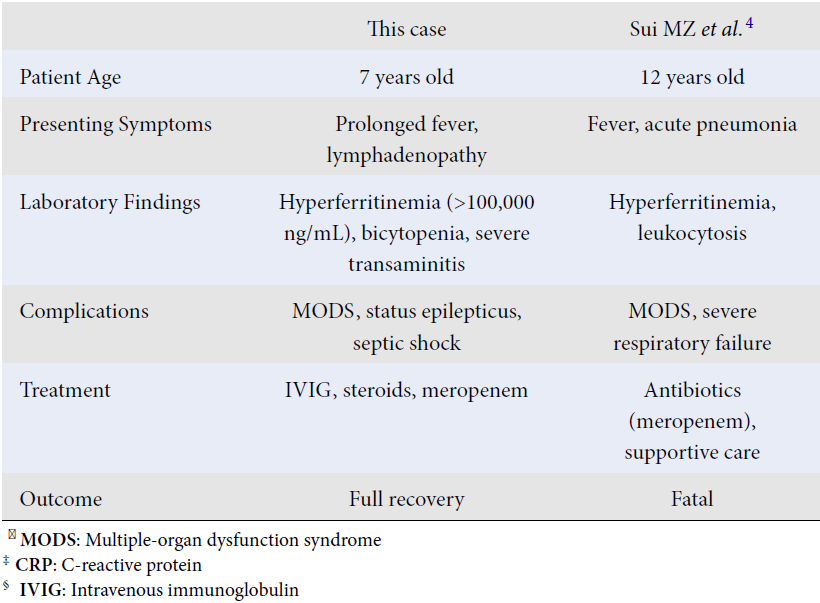
Melioidosis complicating hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: A rare diagnostic entity in paediatric
by Yassin
N., H., M.,
Zain
M., R., M.,
Hamid
I., J., A.,
Kori
A. M. M.
Summary: Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis is a syndrome characterized by excessive immune activation leading to severe systemic inflammation. It encompasses primary and secondary forms, with the latter often triggered by infections. Paediatric cases of melioidosis complicated by hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis are rare and diagnostically challenging.
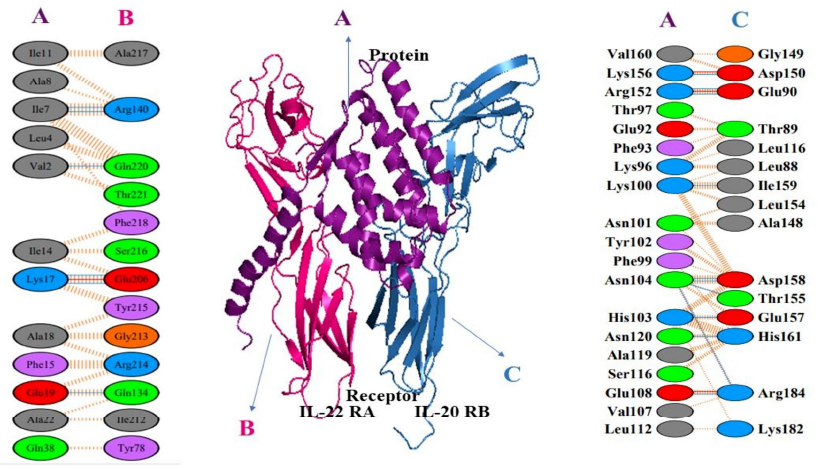
Computational design and evaluation of a novel temporin 1CEa-IL24 fusion protein for anti-tumor potential
by Rehman
H., M.,
Naz
M.,
Ghous
A., G.,
Malik
M.,
Ahmad
S.,
Bashir
H.
Summary: Synthetic fusion proteins represent a cutting-edge approach in biotechnology and pharmaceutical research, enabling the strategic combination of multiple protein domains to design novel complexes with enhanced properties and functionalities. By fusing distinct proteins, the unique attributes of each component can be synergistically exploited, leading to improved bioactivities or the emergence of entirely new functions. This study aimed to computationally construct a fusion protein that contained the killing properties of temporin 1CEa and the targeting action of IL-24, joined via a rigid linker, and its anti-tumor potential was analyzed using different bioinformatics tools.
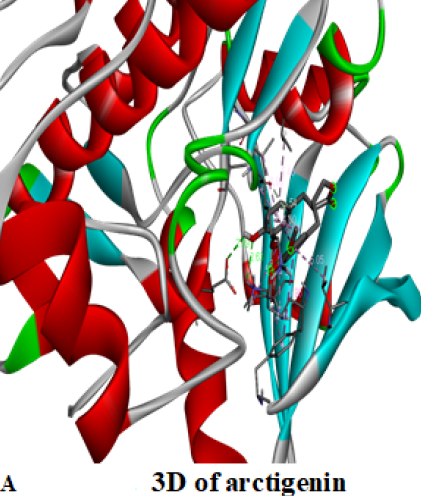
Cytotoxicity and antiproliferative activity of Arctium lappa extract on an in vitro model of human colorectal cancer
by Hassan
A.,
Bondouk
I.,
Abdelrahman
M.,
Saleh
H.
Summary: Natural remedies are an excellent source for screening innovative and safe anti-cancer medicines. This study is intended to explore the potential toxicity of burdock seed extract, Arctium lappa (A. lappa), as well as its anti-regenerative and anti-proliferative effects on tumor cells in vitro.
Upregulation of TPX2 and KIF20A in colorectal cancer
by Ghadiri
F.,
Tajamolian
M.,
Mollanoori
H.,
Babakhanzadeh
E.,
Kargar
S.,
Javid
A.,
Dehghani
M.
Summary: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with metastasis significantly reducing patient survival. Despite advances in treatment, the molecular mechanisms underlying the progression of colorectal cancer remain poorly understood. Recent studies highlight the role of TPX2 and KIF20A, two proteins involved in cell division, in the development of cancer. TPX2 plays a key role in the assembly of the mitotic spindle, while KIF20A is a member of the kinesin superfamily, which is important for intracellular transport and cytokinesis. Both genes are associated with various types of cancer, but their specific contribution to CRC remains unclear. The aim of this study is to investigate the expression and prognostic significance of TPX2 and KIF20A in CRC through bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation.
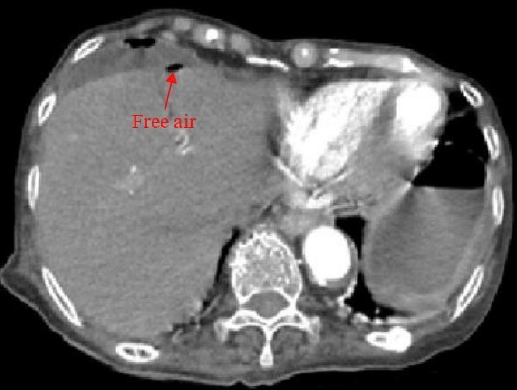
A case report: Perforation of the small intestine and sigmoid colon due to Kirschner wire migration
by Tran
D.,
Pham
T.,
Luu
D.,
Anh
H.,
Nguyen
P., D.,
Nguyen
Q.,
Hoang
H. N.
Summary: Kirschner wires (K-wires) are extensively utilized in orthopedic and trauma procedures. Several risks associated with K-wires have been documented, including a rare case of intestinal perforation caused by wire migration into the pelvis.
Journal Collections

Covid-19 publications
Journal Supplements
Conference Abstracts
Journal Collections

Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine
Special Issues

Special Issues
Journal Collections

Natural Extract
Publication Awards

The best original research articles
Editors' quote

Phuc Van Pham, Editor-in-Chief
Affiliation

Why publish with Biomedical Research and Therapy



 Biomedpress
Biomedpress




